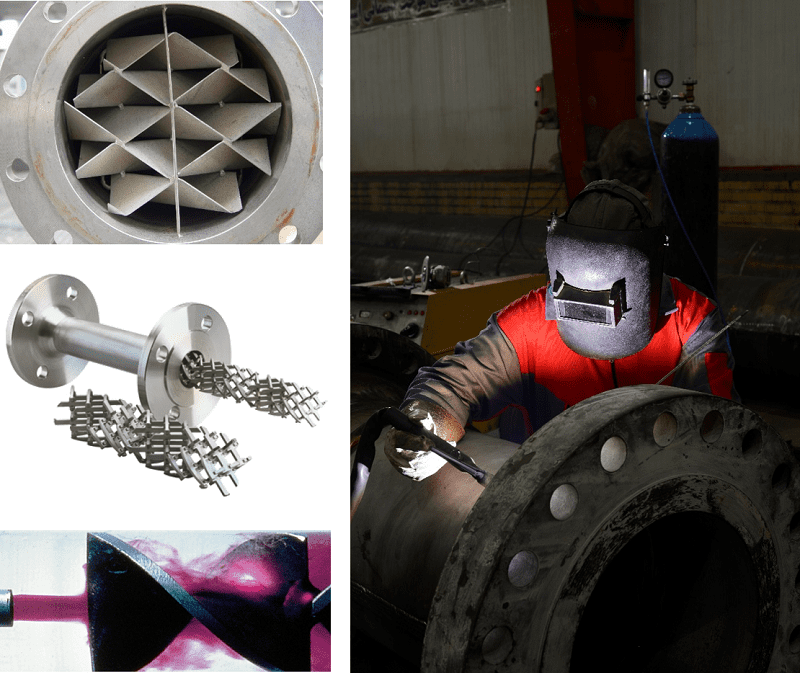
Static mixers, alternatively referred to motionless mixers, are implemented to ensure homogeneity, not only in terms of concentration but also encompassing velocity, temperature, and residence time. Accordingly, they find applications in the fields of blending, dispersion, reaction, and heat transfer. Static mixers operate without any movable components and the required energy for mixing is provided by the fluid pressure itself. By incorporating stationary elements within the pipe, the mixing quality enhances while at the same time, the pressure drop increases.
Static mixers with different shape and structures are employed in both laminar and turbulent in a variety of industries including oil and gas, food, waste water, pulp and paper, adhesive and polymer.
The efficiency of a static mixer is influenced by several factors such as density ratio, viscosity ratio, velocity ratio, inlet droplet size distribution and interfacial surface tension. Therefore, a perfect design must have considered all the parameters exerting an effect on the performance of static mixer.